Drug Nomenclature
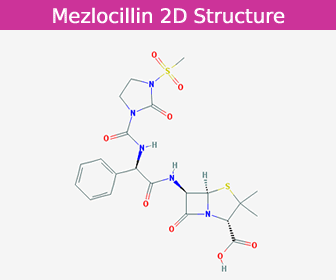
Mezlocillin Sodium
Drug Nomenclature
Pharmacopoeias
The United States Pharmacopeia
A white to pale yellow crystalline powder. Freely soluble in water. pH of a 10% solution in water is between 4.5 and 8.0. Store in airtight containers.
Incompatibility
Mezlocillin sodium has been reported to be incompatible with aminoglycosides, ciprofloxacin, metronidazole, andtetracyclines.
Adverse Effects and Precautions
As for Carbenicillin Sodium. Prolongation of bleeding time has been less frequent and less severe with mezlocillin than with carbenicillin.
Sodium content
Each g of mezlocillin sodium contains about 1.7 mmol of sodium. As mezlocillin sodium has a lower sodium content than carbenicillin sodium, hypernatraemia and hypokalaemia are less likely to occur.
Interactions
As for Benzylpenicillin.
Cefotaxime
For the effect of mezlocillin on the clearance of cefotaxime.
Antimicrobial Action
Mezlocillin has a similar antimicrobial action to piperacillin. Its activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa is less than that of azlocillin or piperacillin.
Pharmacokinetics
Mezlocillin is not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract to any significant extent. It is well absorbed after intramuscular injection, with peak plasma concentrations of 15 to 25 micrograms/mL 45 to 90 minutes after a single dose of 1 g. It is reported to have nonlinear dose-dependent pharmacokinetics.
Between 16 and 42% of mezlocillin in the circulation is bound to plasma proteins. Mezlocillin is reported to have a plasma half-life of about 1 hour; this is slightly prolonged in neonates, and in patients with renal impairment half-lives of up to about 6 hours have been reported. Mezlocillin is widely distributed in body tissues and fluids. It crosses the placenta into the fetal circulation and small amounts are distributed into breast milk. There is little diffusion into CSF except when the meninges are inflamed.
Mezlocillin is reported to be metabolised to a limited extent. About 55% of a dose is excreted unchanged in the urine by glomerular filtration and tubular secretion within 6 hours of a dose, hence achieving high urinary concentrations. High concentrations are also found in the bile; up to 30% of a dose has been reported to be excreted by this route. Plasma concentrations are enhanced by probenecid. Mezlocillin is removed by haemodialysis, and to some extent by peritoneal dialysis.
Uses and Administration
Mezlocillin is a ureidopenicillin with uses similar to those of piperacillin. It is commonly used with an aminoglycoside; however they should be given separately as they have been shown to be incompatible.
Administration and dosage
Mezlocillin is given by injection as the sodium salt. Doses are expressed in terms of the equivalent amount of mezlocillin; 1.07 g of mezlocillin sodium is equivalent to about 1 g of mezlocillin.
Dosage may need to be reduced in renal impairment. It may be given by slow intravenous injection over 3 to 5 minutes, by intravenous infusion over 30 minutes, or by deep intramuscular injection.
Single intramuscular doses should not exceed 2 g. For the treatment of serious infections, 200 to 300 mg/kg daily in divided doses may be given intravenously. For life-threatening infections, up to 350 mg/kg daily may be used, but the total daily dose should not normally exceed 24 g.
For uncomplicated urinary-tract infections, a dose of 1.5 to 2 g may be given intramuscularly or intravenously every 6 hours. Uncomplicated gonorrhoea may be treated by a single intramuscular or intravenous dose of mezlocillin 1 to 2 g. Probenecid 1 g orally may be given at the same time or up to 30 minutes before the injection. For the prophylaxis of infection during surgery, an intravenous pre-operative dose of mezlocillin 4 g, repeated at 6-hourly intervals for 2 further doses, may be given.
Preparations
The United States Pharmacopeia 31, 2008: Mezlocillin for Injection.
Proprietary Preparations
Austria: Baypen; France: Baypen; Germany: Baypen; Israel: Baypen; Italy: Baypen.
Multi-ingredient
Germany: Optocillin

