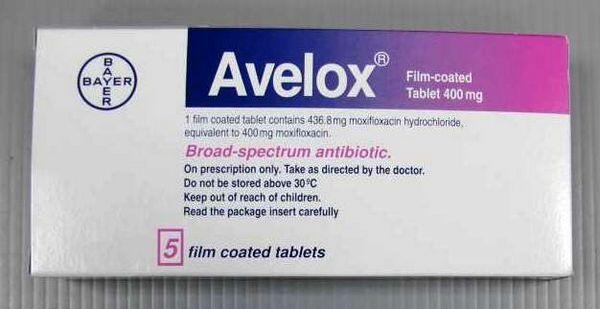
Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride [Avelox 400mg]
Drug Nomenclature
Pharmacopoeias
European Pharmacopoeia
Produced using a method validated to demonstrate the satisfactory enantiomeric purity of the final product. A light yellow or yellow powder or crystals, slightly hygroscopic. Sparingly soluble in water; slightly soluble in alcohol; practically insoluble in acetone. A 0.2% solution in water has a pH of 3.9 to 4.6. Store in airtight containers. Protect from light.
Adverse Effects and Precautions
As for Ciprofloxacin.
Interactions
As for Ciprofloxacin. Moxifloxacin does not appear to interact significantly with theophylline or probenecid.
Antimicrobial Action
As for Ciprofloxacin. Moxifloxacin is reported to have greater activity against Gram-positive bacteria, including pneumococci, than ciprofloxacin.
Pharmacokinetics
Moxifloxacin is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract after oral doses with an absolute bioavailability of about 90%. It is widely distributed throughout the body tissues and is about 30 to 50% bound to plasma proteins. Moxifloxacin has an elimination half-life of about 12 hours, allowing once-daily dosing. It is metabolised mainly via sulfate and glucuronide conjugation, and is excreted in the urine and the faeces as unchanged drug and as metabolites, the sulfate conjugate primarily in the faeces and the glucuronide exclusively in the urine. Distribution into milk has been found in animals.
Uses and Administration
Moxifloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibacterial with actions and uses similar to those of ciprofloxacin. It is given orally, or by intravenous infusion over 60 minutes, for the treatment of susceptible infections including respiratory, skin and skin structure, and intra-abdominal infections. Moxifloxacin is given as the hydrochloride but doses are expressed in terms of the base; moxifloxacin hydrochloride 436.3 mg is equivalent to about 400 mg of moxifloxacin. The usual dose is 400 mg once daily. Moxifloxacin is also used topically as the hydrochloride in eye drops containing the equivalent of 0.5% of moxifloxacin for the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis.
Eye infections
In order to attain therapeutic concentrations most antibacterials used in the treatment of bacterial endoph-thalmitis need to be given by the intravitreal route but moxifloxacin given systemically may produce adequate concentrations. An oral dose of moxifloxacin 400 mg daily may be given for 10 days.
Proprietary Preparations
| Country | Medications |
|---|---|
| Argentina | Avelox; Octegra; Vigamox |
| Australia | Avelox |
| Austria | Actira; Avelox; Octegra |
| Belgium | Avelox; Proflox |
| Brazil | Avalox; Vigamox |
| Canada | Avelox; Vigamox |
| Chile | Avelox; Flovacil; Octegra; Vigamox |
| Czech Republic | Avelox |
| Denmark | Avelox |
| Finland | Avelox |
| France | Izilox |
| Germany | Avalox |
| Greece | Avelox; Octegra; Proflox |
| Hong Kong | Avelox; Vigamox |
| Hungary | Avelox; Octegra |
| India | Moxicip; Moxi |
| Indonesia | Avelox |
| Ireland | Avelox |
| Israel | Megaxin; Vigamox |
| Italy | Actira; Avalox; Octegra |
| Japan | Avelox |
| Malaysia | Avelox; Vigamox |
| Mexico | Avelox; Vigamoxi |
| The Netherlands | Actira; Avelox; Octegra |
| New Zealand | Avelox |
| Philippines | Avelox; Vigamox |
| Poland | Avelox |
| Portugal | Avelox; Proflox |
| Russia | Avelox |
| South Africa | Avelon |
| Singapore | Avelox; Vigamox |
| Spain | Actira; Octegra; Proflox |
| Sweden | Avelox |
| Switzerland | Avalox |
| Thailand | Avelox; Vigamox |
| Turkey | Avelox |
| United Kingdom (UK) | Avelox |
| United States (US) | Avelox; Vigamox |
| Venezuela | Avelox; Vigamox |


 (5 votes, average: 4.60 out of 5)
(5 votes, average: 4.60 out of 5)