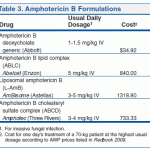
Nystatin is used orally for the treatment of intestinal candidiasis. In patients with coexisting intestinal candidiasis and vulvovaginal candidiasis, nystatin has been administered orally in conjunction with intravaginal application of an antifungal agent. Nystatin has been administered orally as a suspension in conjunction with local application of the drug for the treatment of candidal diaper dermatitis. The majority of infants with candidal diaper dermatitis harbor C. albicans in their intestines, and infected feces appear to be an important source of the cutaneous infection.