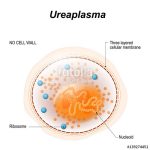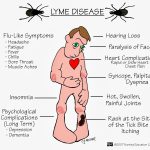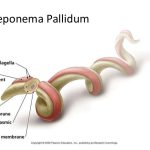
Chlamydia trachomatis, Chlamydia psittaci, and Chlamydia pneumoniae are among the most prevalent microbial pathogens in humans worldwide. C trachomatis is responsible for a variety of sexually transmitted disease (STD) syndromes in both sexes. In addition, certain serotypes of C trachomatis are responsible for trachoma, the most common infectious cause of blindness in humans. C psittaci is a zoonotic pathogen associated with atypical pneumonia.