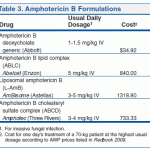
Systematic drug interaction studies have not been performed to date using amphotericin B cholesteryl sulfate complex, amphotericin B lipid complex, or amphotericin B liposomal. The fact that drug interactions reported with conventional IV amphotericin B could also occur with these lipid-based or liposomal formulations of the drug should be considered.