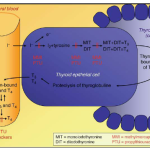
Econazole nitrate is a topical / antifungal agent. It increases cell membrane permeability in susceptible fungi. It is indicated in the treatment of tinea pedis (athlete’s foot), tinea cruris (jock itch), tinea corporis (ringworm), cutaneous candidiasis, and tinea versicolor.