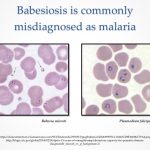
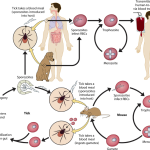
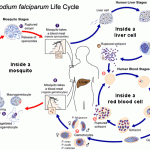
Toxoplasma gondii infection, or toxoplasmosis, is a zoonosis (the definitive hosts are members of the cat family). The two most common routes of infection in humans are by oral ingestion of the parasite and by transplacental (congenital) transmission to the fetus. Ingestion of undercooked or raw meat that contains cysts or of water or food contaminated with oocysts results in acute infection.