What are the primary causes of chronic bronchitis?
Cigarette smoking is cited as the main cause of chronic bronchitis, followed by bacterial or viral infections, air pollution and occupational health hazards, such as exposure to high concentrations of industrial dust and irritating fumes.
What is the difference between emphysema and chronic bronchitis?
Emphysema is the limitation of airflow in and out of the lungs. The disease damages the tiny air sacs in the lungs called alveoli, affecting the lungs’ ability to bring in oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide from the body. Chronic bronchitis occurs when the bronchial tubes in the lungs become inflamed, thickening the walls of the bronchi and narrowing the air passages.
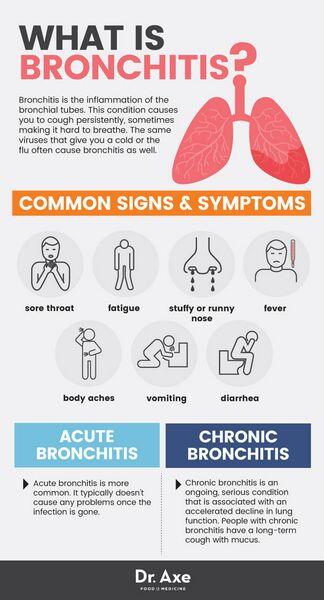
What are the most common symptoms of chronic bronchitis?
Common symptoms may include a cough that produces yellow or green phlegm, wheezing and shortness of breath, frequent and severe respiratory infections, swelling in the legs and feet, and reddish appearance of the face and skin.
How do I know when to get help from a health care professional?
You should contact your healthcare professional when you experience significant changes in your breathing (including bouts of wheezing), or if you have repeated signs of a respiratory infection, such as fever, increased cough or increased mucus production.
How serious is chronic bronchitis?
People suffering from chronic bronchitis often neglect the condition until it is in an advanced state, mainly because they believe the condition is not life threatening. By the time a patient visits a healthcare professional, the disease has already seriously affected the lungs. In these cases, a patient may be in danger of developing long-term respiratory problems or heart failure.
How is chronic bronchitis diagnosed?
In addition to reviewing your complete medical history and performing a physical examination, your healthcare professional may send samples of your phlegm and blood to the laboratory to be tested. The healthcare professional may also take a chest x-ray or perform an exam of your bronchi with an instrument called a bronchoscope. Healthcare professionals also use a pulmonary function test to determine if your lungs are working properly.
Can antibiotics treat chronic bronchitis?
Chronic bronchitis can usually be effectively treated with antibiotics. Your healthcare professional may prescribe LEVAQUIN, an antibiotic used to treat lung, sinus, skin and urinary tract infections caused by certain germs called bacteria. In most patients, LEVAQUIN has been clinically proven to be a safe, well-tolerated and highly effective treatment for chronic bronchitis.
What should I do if I have chronic bronchitis?
See your healthcare professional or follow your healthcare professional’s advice for treating chronic bronchitis, or at the beginning of any cold or respiratory infection. In addition, you should also follow a nutritious, well-balanced diet; exercise regularly (but don’t overexert yourself); avoid exposure to colds at home or in the workplace; avoid respiratory irritants such as dust and other air pollutants; and DON’T SMOKE! Symptoms of chronic bronchitis intensify when people also smoke.
What can I do to help my lungs?
Exercising regularly can help strengthen the muscles that help you breathe. Start out by exercising slowly and for just a short while, increasing the time and energy level you exercise each day. You might begin exercising by walking slowly for 15 minutes, three times a week. As you get in better shape, you can increase your walking speed and length of time you walk to 20 minutes. Add five minutes of time each day until you reach a comfortable cardiovascular workout.