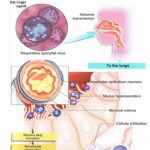
Inflammation of the bronchioles, usually seen in young children, occasionally in high-risk adults. May be seasonal (winter and spring) and often occurs in epidemics.

Despite the large patient populations with respiratory tract infections (RTIs), in recent years, many biopharmaceutical companies have shifted development effort away from RTIs to pursue other disease areas with perceived higher unmet need (e.g., resistant hospital-acquired infections). Likewise, many companies have shifted away from antibacterial drug development in favor of chronic disease markets perceived to have higher return on investment.
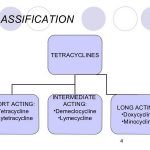
Tetracyclines are the prototypical broad-spectrum antibiotic and are occasionally used as first-line agents in some markets (e.g., Germany) for the treatment of mild acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis, particularly when cost, penicillin hypersensitivity, and β-lactam resistance are of concern. The widespread use of tetracyclines has resulted in a steady increase in the prevalence of resistance to these agents. Therefore, empiric use of tetracyclines is usually restricted to regions where resistance levels remain low or when other appropriate antibiotics are contraindicated.