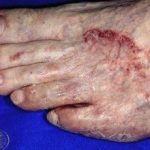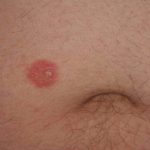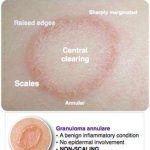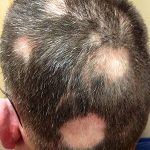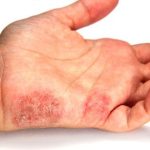
The anthropophilic dermatophytes E. floccosum, T. mentagrophytes var. interdigitate and T. rubrutn are the most common causes of tinea manuum. Less commonly, the condition is caused by zoophilic dermatophytes, such as M. canis and T. verrucosum, or geophilic dermatophytes, such as M. gypseum. Hand infection may be acquired as a result of contact with another person, with an animal, or with soil, either through direct contact, or via a contaminated object such as a towel or gardening tool. Autoinoculation from another site of infection can also occur.