
Penicillins: Organs and Systems. Respiratory, Nervous system, Gastrointestinal, Urinary tract.

Anaphylactic shock can occur, even after oral administration of penicillin and skin testing. However, anaphylactic shock is less common after oral than parenteral administration. In one study the incidence of anaphylactic shock was 0.04% of all patients treated with penicillin. It is also low in patients receiving long-term benzathine penicillin (1.2 million units every 4 weeks).

Skin reactions are the commonest adverse effects of therapeutically administered penicillins. Penicillin-contaminated milk or meat can cause itching or generalized skin reactions or even anaphylaxis. The overall annual incidence of severe erythema multi-forme (toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome) is about one case per million, antibiotics being involved in 30-40%. The clinical differentiation between these syndromes can be difficult.
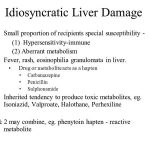
Penicillin-induced hepatotoxicity may not be as uncommon as has been thought. There have been three reviews. The first was a comparison of the assessment of drug-induced liver injury obtained by two different methods, the Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences (CIOMS) scale and the Maria & Victorino (M&V) clinical scale. Three independent experts evaluated 215 cases of hepatotoxicity reported using a structured reporting form.

Since the days when chloramphenicol was more commonly used, it has been recognized that many antimicrobial drug are associated with severe blood dyscrasias, such as aplastic anemia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, throm-bocytopenia, and hemolytic anemia. Information on this association has come predominantly from case series and hospital surveys (38^. Some evidence can be extracted from population-based studies that have focused on aplastic anemia and agranulocytosis and their association with many drugs, including antimicrobial drugs. The incidence rates of blood dyscrasias in the general population have been estimated in a cohort study with a nested case-control analysis, using data from a General Practice Research Database in Spain.
Chloroquine and its congeners can cause two typical effects in the eye, a keratopathy and a specific retinopathy. Both of these effects are associated with the administration of the drug over longer periods of time. Chloroquine-induced keratopathy is limited to the corneal epithelium, where high concentrations of the drug are readily demonstrable. Slit lamp examination shows a series of punctate opacities scattered diffusely over the cornea; these are sometimes seen as lines just below the center of the cornea, while thicker yellow lines may be seen in the stroma.

The “gray syndrome” is the term given to the vasomotor collapse that occurs in neonates who are given excessive parenteral doses of chloramphenicol. The syndrome is characterized by an ashen gray, cyanotic color of the skin, a fall in body temperature, vomiting, a protuberant abdomen, refusal to suck, irregular and rapid respiration, and lethargy. It is mainly seen in newborn infants, particularly when premature.

Albendazole has been used in the treatment of human hookworm and trichuriasis. In a mass-treatment report from Western Australia 295 individuals in a remote rural area were treated with albendazole 400 mg/day for 5 days because of possible Giardia lamblia and hookworm infections. The 37% prevalence of Giardia fell to 12% between days 6 and 9, but rose again to 28% between days 18 and 30. The effect on hookworms (Ankylostoma duodenale) was more pronounced and more sustained with a reduction of the pretreatment prevalence of hookworm infections from 76% before treatment to 0% after 3^1 weeks.
Among the published studies some have specifically sought to define the pattern of adverse effects. In one such study, although a single dose of the drug was combined in some patients with diethylcarbamazine, the adverse effect pattern was similar to that when ivermectin was used alone. There now seem to be some circumstances in which a single low dose of ivermectin is sufficient to have a prolonged effect, for example in loaiasis a dose of 150 micrograms/kg resulted in a very much reduced level of microfilaria as much as a year later, and seemed to eliminate the infestation entirely in more than half the users. If further work confirms the validity of this approach, the adverse reactions problem may be lessened, since at these doses the few reactions experienced were limited to the skin and joints, although some calabar-like swellings were also noted.