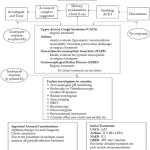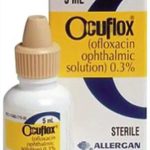
Ofloxacin ophthalmic is one of the medications to treat bacterial infections of the eye. The main active ingredient is also used in the Ofloxacin ear drops, which proved their effectiveness over time. Both remedies are to be applied with precaution and according to the prescription.