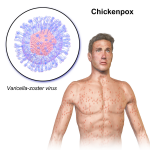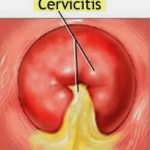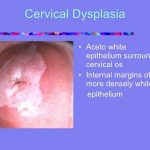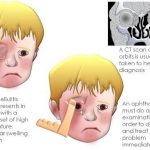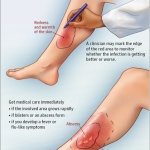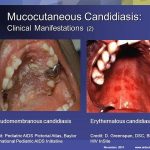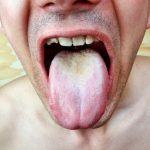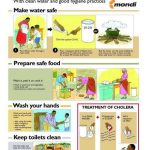
An acute infectious disease caused by Vibrio cholerae (El Tor type is responsible for current epidemic, the other type, classic, is found only in Bangladesh). (New serotype now in Bangladesh, India (0139). Important because of lack of efficacy of standard vaccine.) Characteristics include severe diarrhea with extreme fluid and electrolyte depletion, and vomiting, muscle cramps and prostration.