
Systemic bacterial infection caused by Brucella species in infected animal products, or vaccine. Incubation period usually 5-60 days, but highly variable and may be several months.
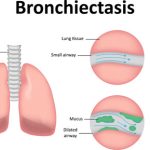
Conditions that may lead to bronchiectasis include severe pneumonia (especially measles, pertussis, adenoviral infections in children), necrotizing infections due to Klebsiella, staphylococci, influenza virus, fungi, mycobacteria, mycoplasma, bronchial obstruction from any cause (foreign body, carcinoma, enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes.
An intoxication producing paralytic disease caused by neurotoxins of Clostridium botulism and is the most toxic substances known to science. The toxin prevents acetylcholine release at presynaptic membranes, blocking neuromuscular transmission in cholinergic nerve fibers. Electro my ogram (EMG) shows characteristic brief, low voltage compound motor-unit, small amplitude, overly abundant action potentials (BSAPs), incremental response to repetitive stimulation. Findings not definitive for botulism.
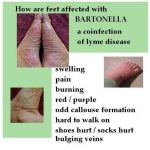
Blood cultures: lysis-centrifugation (Isolator) cultures plated on blood or chocolate agar, incubated at 35-37°C in 5% C02 > 2 weeks; enriched broth media, e.g. BACTER, incubated at 35-37°C in 5% C02 >2 weeks and subculture to agar if bacilli detected by periodic acridine orange staining. Avoid contact with potential vectors, especially young cats.
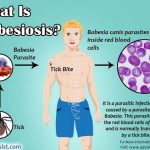
Several other drugs have been evaluated, including tetracycline, primaquine, sulfadiazine (Microsulfon) and pyrimethamine (Fansidar). Results have varied. Pentamidine (Pentam) has proved to be moderately effective in diminishing symptoms and decreasing parasitemia. Others: High-level parasitemia is more common in asplenic patients.