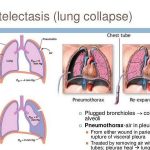
Atelectasis (lung collapse) is a portion of lung which is non-aerated, but otherwise normal. May be an asymptomatic finding on CXR or associated with symptoms.
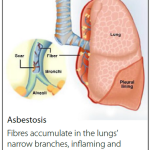
A chronic non-malignant lung disease caused by inhalation of asbestos, a hazardous dust found in a variety of work places. This disease persists in spite of substantial knowledge about its cause, and effective means of prevention. The disease typically occurs 10-15 years after initial exposure. Asbestosis is a fibrotic interstitial lung disease caused by a cascade of responses to inhaled asbestos fibers.
Amebiasis is caused by the intestinal protozoan, Entamoeba histolytica. Infection results from ingestion of fecally contaminated food, such as garden vegetables or by direct fecal-oral transmission. Most persons are asymptomatic or have minimal diarrheal symptoms. In a few patients, invasive intestinal or extraintestinal (e.g., liver, and less commonly kidney, bladder, male or female genitalia, skin, lung, brain) infection results.

Usually self-limited febrile illnesses characterized by inflammation of conjunctivae and the respiratory tract. Adenovirus infections occur in epidemic and endemic situations. Incidence/Prevalence in USA: Very common infection, estimated at 2-5% of all respiratory infections. More common in infants and children.
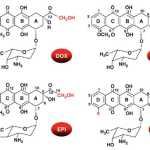
The anthracyclines are composed of a tetracyclic ring with adjacent quinone-hydroquinone moieties and a short side chain with a carbonyl group at C-13; an aminosugar is attached by a glycosidic bond to the C-7 of the tetracyclic ring. Doxorubicin (DOX) and daunorubicin (DNR) differ in the side chain terminus (-CH2OH or-CH3, respectively).