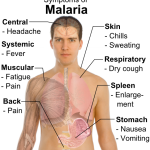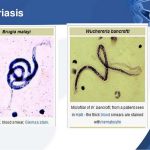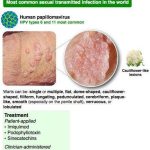
Condyloma acuminata are soft skin colored, fleshy warts that are caused by the HPV (human papilloma virus). There are now > 100 known types of HPV and types 6, 11,16,18, 31, 33, 35 have been associated with condyloma acuminata. The disease is highly contagious, can appear singly or in groups, small or large. They appear in the vagina, on the cervix, around the external genitalia and rectum, in the urethra, anus, also conjunctival, nasal, oral and laryngeal warts and occasionally, the throat.