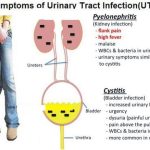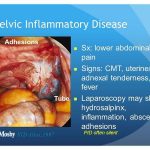
PID is a clinical syndrome caused by the ascent of microorganisms from the vagina and endocervix to the endometrium, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and contiguous structures. PID is a broad term that includes a variety of upper genital tract infections, unrelated to pregnancy or surgical procedures, such as salpingitis, salpingo-oophoritis, endometritis, tubo-ovarian inflammatory masses, and pelvic or diffuse peritonitis. The precise mechanism by which microorganisms ascend from the lower genital tract is not known. One possibility is that chlamydial or gono-coccal endocervicitis alters the defense mechanisms of the cervix allowing ascent of the vaginal flora with or without the original pathogen.