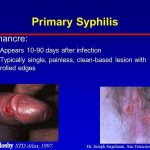
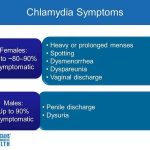
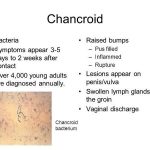
The spectrum of sexually transmitted diseases includes the classic venereal diseases – gonorrhea, syphilis, chancroid, lymphogranuloma venereum, and granuloma inguinale – as well as a variety of other pathogens known to be spread by sexual contact (Table Sexually Transmitted Diseases). Common clinical syndromes associated with sexually transmitted diseases are listed in Table Selected Syndromes Associated with Common Sexually Transmitted Pathogens.