General principles
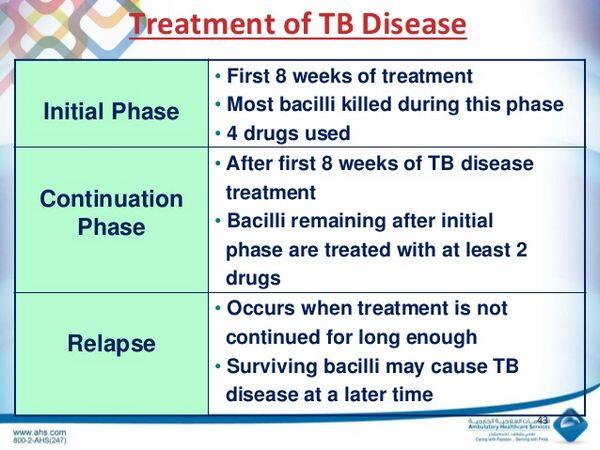
- Drug treatment is the cornerstone of Tuberculosis management. A minimum of two drugs, and generally three or four drugs, must be used simultaneously.
- Drug treatment is continued for at least 6 months and up to 2 to 3 years for some cases of multidrug-resistant Tuberculosis (MDR-Tuberculosis).
- Measures to assure adherence, such as directly observed therapy (DOT), are important.
Pharmacologic treatment
Latent Infection
- Chemoprophylaxis should be initiated in patients to reduce the risk of progression to active disease.
- Isoniazid, 300 mg daily in adults, is the primary treatment for latent Tuberculosis in the United States, generally given for 9 months.
- Individuals likely to be noncompliant may be treated with a regimen of 15 mg/kg (to a maximum of 900 mg) twice weekly with observation.
- If the individual has been exposed to a patient with Isoniazid-resistant M. tuberculosis or a patient who has failed chemotherapy, chemoprophylaxis with rifampin (for 4 months) should be initiated.
- Pregnant women, alcoholics, and patients with poor diets who are treated with isoniazid should receive pyridoxine, 10 to 50 mg daily, to reduce the incidence of central nervous system (central nervous system) effects or peripheral neuropathies.
Treating Active Disease
- Appropriate samples should be sent for culture and susceptibility testing prior to initiating therapy. Drug susceptibility testing should be done on the initial isolate for all patients with active Tuberculosis, and this data should guide the initial drug selection for the new patient. If the source case cannot be identified, the drug resistance pattern in the area where the patient likely acquired Tuberculosis should be used.
- If the patient is being evaluated for the retreatment of Tuberculosis, it is imperative to know what drugs were used previously and for how long.
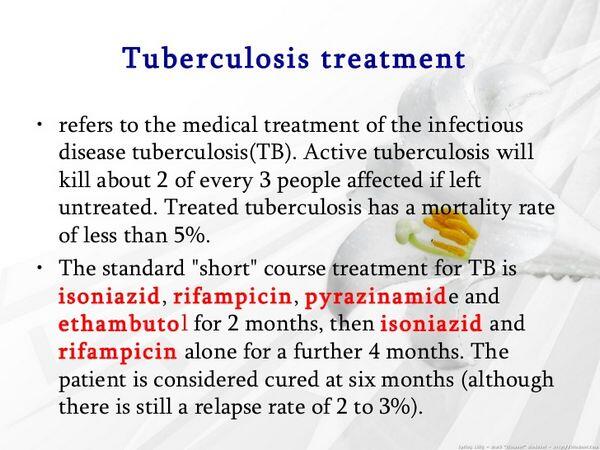
- Patients must complete 6 months or more of treatment. HIV-positive patients should be treated for an additional 3 months and at least 6 months from the time that they convert to smear and culture negativity. When isoniazid and rifampin cannot be used, treatment duration becomes 2 years or more, regardless of immune status.
| TABLE. Recommended Drug Regimens for Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TABLE. Drug Regimens for Culture-Positive Pulmonary Tuberculosis Caused by Drug-Susceptible Organisms | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TABLE. Dosesa of Antituberculosis Drugs for Adults and Childrenb | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- If the organism is drug resistant, the aim is to introduce two or more active agents that the patient has not received previously. With MDR-Tuberculosis, no standard regimen can be proposed. It is critical to avoid monotherapy or adding only a single drug to a failing regimen.
Drug Resistance
Drug resistance should be suspected in the following situations:
- Patients who have received prior therapy for Tuberculosis
- Patients from geographic areas with a high prevalence of resistance (New York City, Mexico, Southeast Asia, and the former Soviet states)
- Patients who are homeless, institutionalized, intravenous drug abusers, and/or infected with HIV
- Patients who still have acid-fast bacilli (AFB)-positive sputum smears after 2 months of therapy
- Patients who still have positive cultures after 3 to 4 months of therapy
- Patients who require retreatment
Special Populations
Tuberculous meningitis and Extrapulmonary disease
In general, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, ethionamide, and cycloserine penetrate the cerebrospinal fluid readily. Patients with central nervous system tuberculosis are often treated for longer periods (9 to 12 months). Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis of the soft tissues can be treated with conventional regimens. Tuberculosis of the bone is typically treated for 9 months, occasionally with surgical debridement.
Children
Tuberculosis in children may be treated with regimens similar to those used in adults, although some physicians still prefer to extend treatment to 9 months.
Pregnant women
- The usual treatment of pregnant women is isoniazid, rifampin, and ethambutol for 9 months.
- Women with Tuberculosis should be cautioned against becoming pregnant, as the disease poses a risk to the fetus as well as to the mother. Isoniazid or ethambutol are relatively safe when used during pregnancy. Supplementation with B vitamins is particularly important during pregnancy. Rifampin has been rarely associated with birth defects, but those seen are occasionally severe, including limb reduction and central nervous system lesions. Pyrazinamide has not been studied in a large number of pregnant women, but anecdotal information suggests that it may be safe. Ethionamide may be associated with premature delivery, congenital deformities, and Down’s syndrome when used during pregnancy. Streptomycin has been associated with hearing impairment in the newborn, including complete deafness.
HIV-infected patients
AIDS patients and other immunocompromised hosts may be managed with chemotherapeutic regimens similar to those used in immunocompetent individuals, although treatment is often extended to 9 months.
Renal failure
In nearly all patients, isoniazid and rifampin do not require dose modifications in renal failure. Pyrazinamide and ethambutol typically require a reduction in dosing frequency from daily to three times weekly (Table Dosing Recommendations for Adults Patients with Reduced Renal Function and for Adult Patients Receiving Hemodialysis).
| TABLE. Dosing Recommendations for Adults Patients with Reduced Renal Function and for Adult Patients Receiving Hemodialysis | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||