Description of Medical Condition

- Cervicitis — inflammatory changes due to infections
- Ectropion — eversion of the cervix in pregnancy
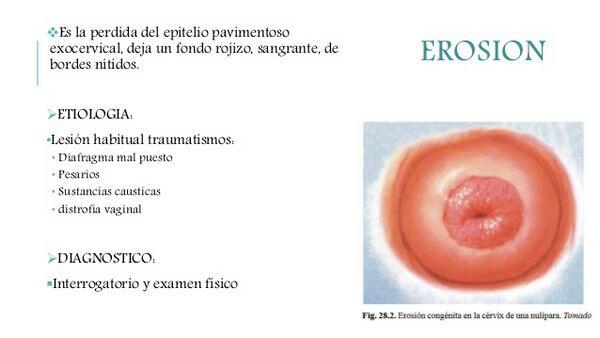
- True erosion — loss of overlying vaginal epithelium due to trauma, e.g., forceful insertion of vaginal speculum in patient with atrophic mucosa
System(s) affected: Reproductive
Genetics: N/A
Incidence/Prevalence in USA:
- Cervicitis — very common in sexually active women
- Ectropion — with oral contraceptive use; very common in pregnant women
- True erosion — occasionally seen in postmenopausal women
Predominant age: Sexually active women
Predominant sex: Female only
Medical Symptoms and Signs of Disease
- Cervicitis — metrorrhagia, post-coital bleeding, vaginal discharge
- Ectropion — red cervix due to color of the columnar epithelium
- True erosion — vaginal bleeding, sharply defined ulcers of cervix
What Causes Disease?
- Cervicitis — Chlamydia trachomatis, Trichomonas vaginalis
- Ectropion — hormonal changes with oral contraceptive use (especially with progesterone) or during pregnancy
- True erosion — injury to atrophic epithelium due to estrogen deficiency in menopause
Risk Factors
-
- Cervicitis — sexual contact with infected partner(s). recurrence due to inadequate therapy
- Ectropion — pregnancy
- True erosion — estrogen deficiency, trauma
Diagnosis of Disease
Differential Diagnosis
- Cervical dysplasia
- Carcinoma of the cervix
Laboratory
- Saline and potassium hydroxide preparation of cervical/vaginal smears
- Chlamydiazyme or chlamydia cell culture, gonorrhea culture
- Papanicolaou (Pap) smear of the cervix
- Chlamydia DNA probe
- Gonorrhea DNA probe
Drugs that may alter lab results: N/A
Disorders that may alter lab results: N/A
Pathological Findings
- Cervicitis — acute and chronic inflammatory changes, presence of infective organisms
- Ectropion — none/squamous metaplasia
- True erosion — sharply defined ulcer borders, loss of epithelium
Special Tests
None
Imaging
None
Diagnostic Procedures
Colposcopy
Treatment (Medical Therapy)
Appropriate Health Care
Outpatient
General Measures
N/A
Activity
No restrictions
Diet
No special diet
Patient Education
Provide printed material about sexually transmitted diseases and about estrogen deficiency and estrogen replacement therapy
Medications (Drugs, Medicines)
Drug(s) of Choice
- Trichomoniasis — metronidazole 500 mg bid for 7 days or 2 g once or 1 g bid for 2 doses
- Chlamydial infection — for non-pregnant women, doxycycline 100 mg bid po for 7 days; for pregnant women, erythromycin base 500 mg qid po for 7 days, or erythromycin ethylsuccinate 800 mg qid for 7 days
- Ectropion — none
- True erosion — estrogen, conjugated vaginal cream daily for 2 weeks, followed by estrogen replacement therapy
Contraindications:
- Metronidazole — first trimester of pregnancy
- Doxycycline — pregnancy or lactation
- Estrogen — see extended list of contraindications to estrogen use in standard texts
Precautions:
- Metronidazole — possible fetal harm if used in first trimester of pregnancy, disulfiram reaction with alcohol
- Doxycycline — possible fetal harm if used during pregnancy, staining of the infant’s teeth if used during breast-feeding, allergy, photosensitization
- Erythromycin — nausea or vomiting
- Estrogens — history of estrogen dependent neoplasms, history of thromboembolic diseases, see extended list of contraindications to estrogen therapy in standard texts
Significant possible interactions:
- Metronidazole and alcohol
- Doxycycline and dairy products, iron preparations, warfarin, and oral contraceptives (use backup contraceptive method)
- Erythromycin with astemizole — may increase latter’s levels with subsequent ECG changes
- Erythromycin and theophylline (elevated theophylline level)
- Estrogen — N/A
Alternative Drugs
- Metronidazole — sulfanilamide-aminacrine-allantoin cream (AVC cream)
- Doxycycline — erythromycin or azithromycin
- Erythromycin — clindamycin
- Estrogen — lubricant, same as that used for vaginal speculum
- Azithromycin 1 g for one dose only (pregnancy category B)
- Ofloxacin 300 mg bid x 7 days
- Amoxicillin-clavulanate (Augmentin) 250 mg po q8h for 7 days
Patient Monitoring
- Trichomoniasis — repeat vaginal smear until infection is cleared
- Chlamydial infection — repeat chlamydial culture post antibiotic therapy
- Estrogen deficiency — re-examine in one month to confirm healing
Prevention / Avoidance
- Trichomoniasis or chlamydial infection — treatment of sexual partners and use of condom during coitus
- Estrogen deficiency — estrogen replacement therapy
Possible Complications
N/A
Expected Course / Prognosis
- Cervicitis — excellent healing once infection is eradicated
- Ectropion — spontaneous regression postpartum, cessation or oral contraceptive use
- True erosion — spontaneous healing
Miscellaneous
Associated Conditions
- Gonorrhea
- Bacterial vaginosis
Age-Related Factors
Pediatric: N/A
Geriatric: Menopause
Pregnancy
- Ectropion
- Azithromycin should be used with caution
- Doxycycline should not be used in pregnancy
International Classification of Diseases
616.0 Cervicitis and endocervicitis



